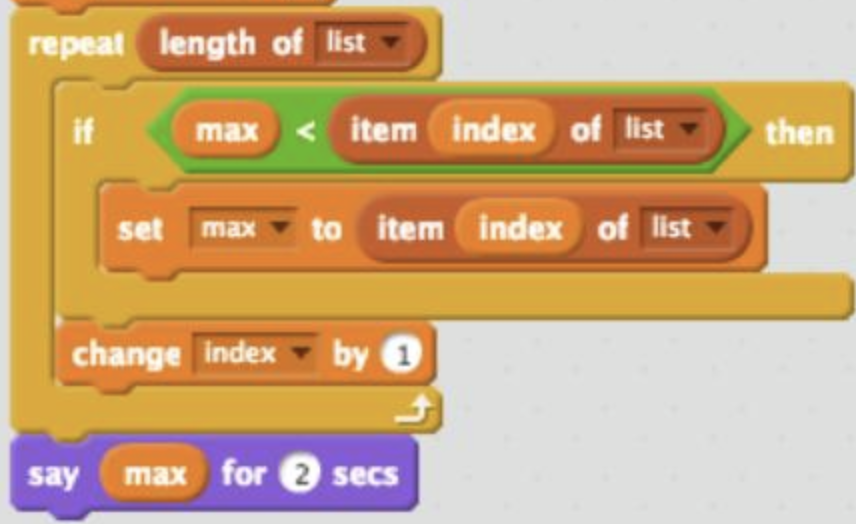
It is quite challenging to access to videos for people who are blind or have low vision (BLV), particularly creating audio descriptions that describe the scenes without interfering the dialogues in a video. There is also the challenge of providing additional information using multi-modal feedback, that is using non-speech audio and haptics.