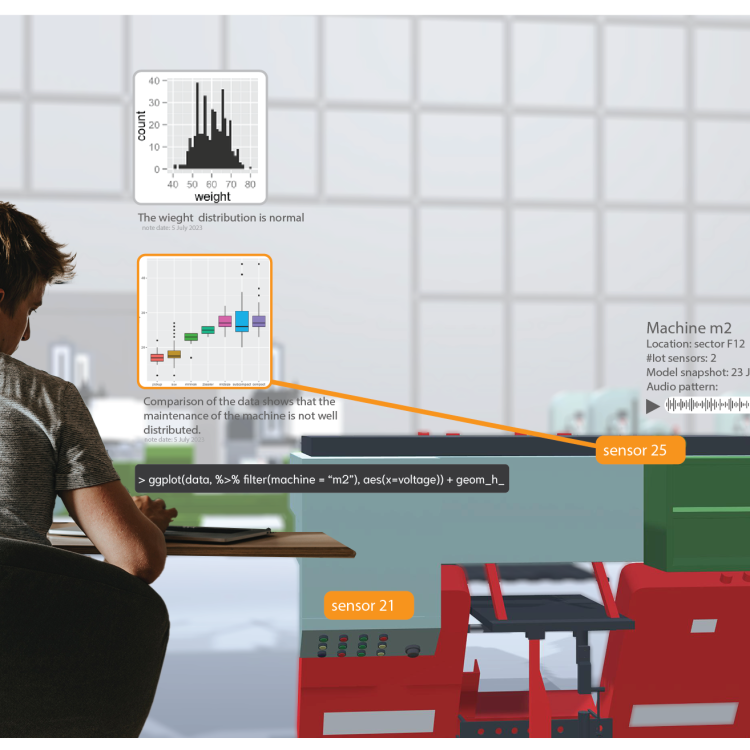
Our industry partners are developing software for automation of Hydrogen Deuterium Mass Spectrometry, which can connect structure, behaviour and function of proteins, for understanding diseases and developing drug and vaccine treatments.
Modern AI techniques can provide powerful models for classifying and understanding protein structures, but expert supervision is required in the development, training and deployment of these models into automation scenarios.