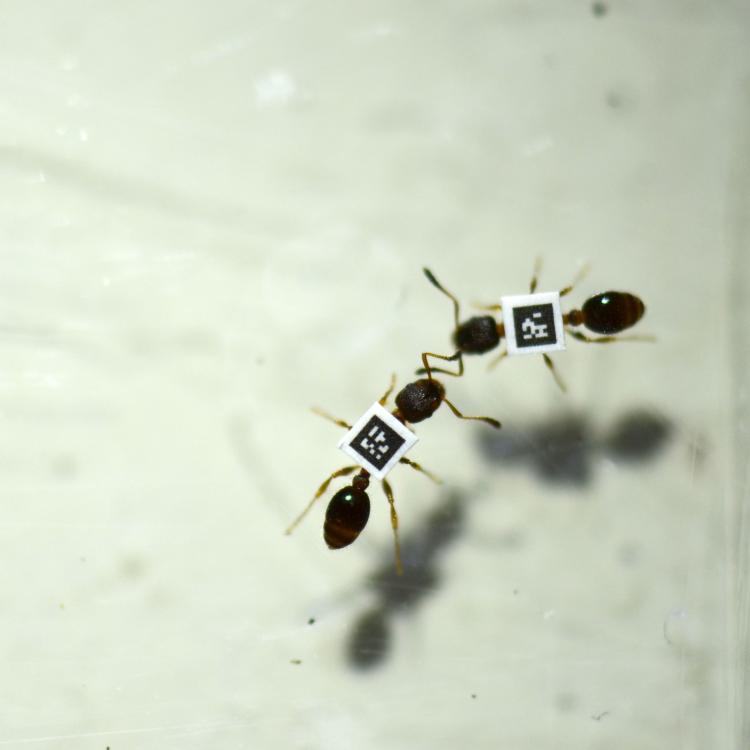
Species’ distributions are shifting in response to global climate change and other human pressures. Accurate methods to monitor and predict distribution shifts are urgently needed to manage threatened species and ecosystems, and to control invasive species and diseases. This requires a step-change in the data and methods used to monitor and predict organism behaviours and ultimately shifts in species' distributions.
Research projects in Information Technology
Displaying 81 - 90 of 112 projects.
Visual aids for human reasoning with causal Bayesian networks
This PhD project is funded by a successful ARC Discovery Project grant: "Improving human reasoning with causal Bayesian networks: a user-centric, multimodal, interactive approach" and the successful applicant will work as part of a larger research team.
Reinforcement Learning for Self-organised Task Allocation
Effective allocation of tasks is essential for any socially living group. This project investigates self-organised task allocation, ie groups in which tasks are not centrally assigned to individuals. In self-organised groups, individuals rather select their tasks autonomously based on their own choices and preferences. Under which conditions does this achieve the desired group outcomes?
Image analysis in forensic pathology
We have a range of potential research projects on offer in partnership with VIFM - https://www.vifm.org/ - looking at ML techniques in predicting forensic diagnoses / image analysis, across multiple data types found at VIFM. These include atomic data, text data and text documents, medical images, clinical photographs and digital pathology slides.
This research has high potential to support our IT for social good agenda in addition to its technical attractiveness.
Efficient Incrementality in Learning Solvers
Reasoning, constraint solving and optimisation technologies have made remarkable progress over the last two decades. A number of formalisms like Boolean satisfiability (SAT), satisfiability modulo theories (SMT) and their optimisation extensions (MaxSAT and MaxSMT) as well as constraint programming and optimisation (CP) and mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) can be seen as success stories in computer science.
Learning in a dynamic and ever changing world
The world is dynamic, in constant flux. However, machine learning typically learns static models from historical data. As the world changes, these models decline in performance, sometimes catastrophically so. This PhD will develop technologies for addressing this serious problem, building upon our groundbreaking research into the problem.
Unlocking time: machine learning for understanding dynamic processes
The world is dynamic and in a constant state of flux, yet most machine learning models learn static models from a dataset that represents a single snapshot in time. My group's research is revolutionising the field of temporal analytics. We have refocused the field on methods that are both effective and feasible for non-trivial problems.
Computational drug discovery
This project works with leading researchers in the Faculty of Pharmacy to develop new artificial intelligence technologies to aide discovery of drugs to treat pharmacoresistant epilepsy.
Research and development data infrastructure for Law Enforcement
This project concerns the investigation of suitable socio-technical data infrastructure for law-enforcement research and development. International collaboration between law-enforcement agencies, research institutions, and commercial organisations is vital to address the large scale technical challenges inherent in combating criminal network activity. A significant issue in this work concerns the data infrastructure necessary for collaborative research into, and development of, analytical techniques and algorithmic models.
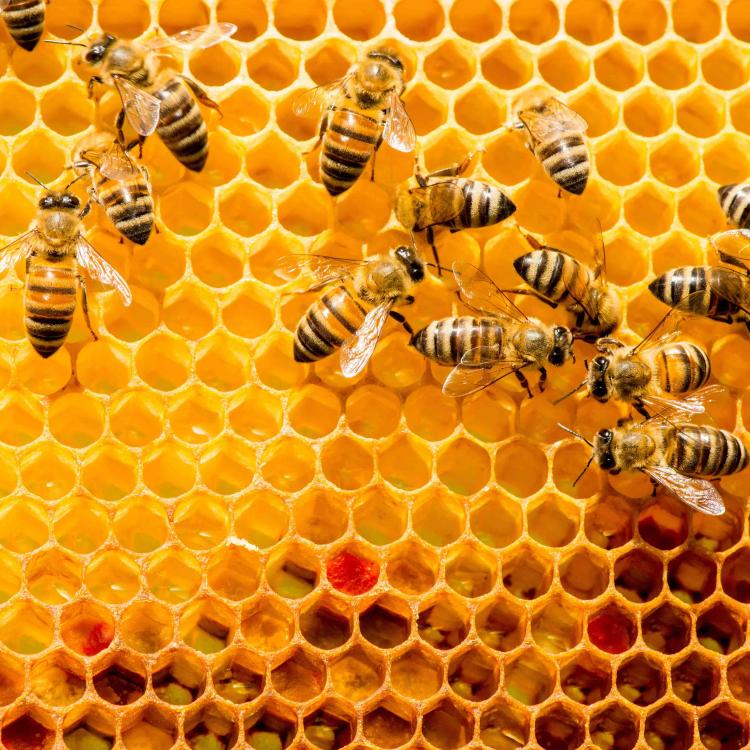
Save the Bees, one buzz at a time
In this project, we will use machine learning methods to diagnose the health status of bee colonies and individual bees.
Bee populations are threatened worldwide due to a number of factors, including parasites and virus infections, climate change, intensive farming, and other environmental stress factors. Australia, until recently, has been relatively protected from infections, but these are now increasingly taking place here as well.