The United Nations Development Programme has identified access to information as an essential element to support poverty eradication. People living in poverty are often unable to access information that is vital to their lives, such as information on their entitlements, public services, health, education or work opportunities. Timely access to information is essential to perform many economic, social and leisure activities. In today’s digital age, information is more and more often provided in digital form.
Research projects in Information Technology
Displaying 121 - 130 of 198 projects.
Complex question answering & generation over knowledge graphs
Complex questions are those that involve discrete, aggregate operators that operate on numbers (min, max, arithmetic) and sets (intersection, union, difference). Recent advances in complex question answering take a neural-symbolic approach and combine meta-learning and reinforcement learning techniques [1,2,3]. On the other hand, the generation of complex questions, the dual problem, is less explored. Recent works on knowledge graph question generation [4,5] have mainly focussed on multi-hop questions.
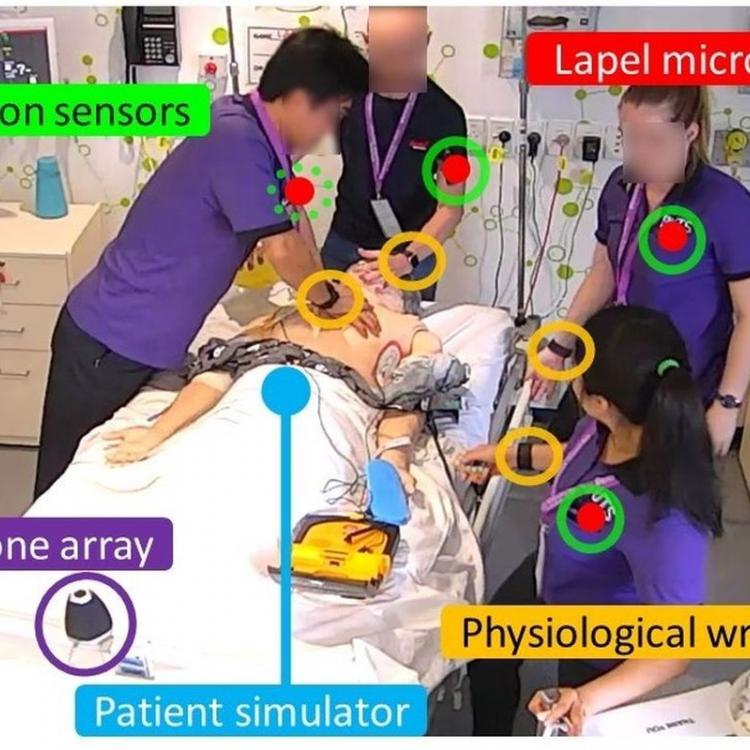
Human-Centred Multimodal Teamwork Analytics
This scholarship will provide a stipend allowance of $29,000 AUD per annum for up to 3.5 years, plus $4,000 travel allowance. If you are currently in Australia you are strongly encouraged to apply. If successful, you will join Dr. Roberto-Martinez Maldonado, Prof. Dragan Gasevic, and a strong team of academics, researchers and other students at the Centre of Learning Analytics at Monash University, Melbourne.
ITTC OPTIMA projects
The Australian Research Council (ARC) Training Centre in Optimisation Technologies, Integrated Methodologies, and Applications (OPTIMA) is seeking applications for ten ARC fully-funded PhD projects with generous top-up scholarships.
We're looking for talented students with a background in mathematics, computer science, statistics, economics, engineering or other related fields. These positions are offered across OPTIMA's nodes located at Monash University or The University of Melbourne. Projects will be available from June 2021 onwards.
Precision medicine for paediatric brain cancer patients
The proposed PhD project aims to build a machine learning/deep learning-based decision support system that provides recommendations on precision medicine for paediatric brain cancer patients based on clinical, genomics and functional dependency data (CRISPR, drug screens).
Anomaly detection in evolving (dynamic) graphs
Anomaly detection is an important task in data mining. Traditionally most of the anomaly detection algorithms have been designed for ‘static’ datasets, in which all the observations are available at one time. In non-stationary environments on the other hand, the same algorithms cannot be applied as the underlying data distributions change constantly and the same models are not valid. Hence, we need to devise adaptive models that take into account the dynamically changing characteristics of environments and detect anomalies in ‘evolving’ data.
Clustering of (time series of) generalised dynamic Bayesian nets, etc.
The relationship between the information-theoretic Bayesian minimum message length (MML) principle and the notion of Solomonoff-Kolmogorov complexity from algorithmic information theory (Wallace and Dowe, 1999a) ensures that - at least in principle, given enough search time - MML can infer any underlying computable model in a data-set.
A consequence of this is that we can (e.g.)
Does deep learning over-fit - and, if so, how does it work?
Methods of balancing model complexity with goodness of fit include Akaike's information criterion (AIC), Schwarz's Bayesian information criterion (BIC), minimum description length (MDL) and minimum message length (MML) (Wallace and Boulton, 1968; Wallace and Freeman, 1987; Wallace and Dowe, 1999a; Wallace, 2005).
Re-visiting hypothesis testing
There are many approaches to hypothesis testing. The well-known approach of p-values has been drawn into question and even controversy in more recent years, even though criticisms reportedly date back at least as far as 1954 (Dowe, 2008a, sec. 1, pp549-550).
Discussion of how to do this using the Bayesian information-theoretic minimum message length (MML) approach (Wallace and Boulton, 1968; Wallace and Dowe, 1999a; Wallace, 2005) are given in Dowe (2008a, section 0.2.5, page 539, and section 0.2.2, page 528), and Dowe (2011, pages 919 and 964).
Machine learning analysis of gravitational waves
The recent discovery in 2015 of gravitational waves from colliding black holes and neutron stars has opened a new window on the Universe. Astrophysicists can now “see the unseeable” -- black holes that emit no light are regularly being observed through their gravitational-wave signatures. Since the first discovery in 2015, more than 50 black hole mergers, two neutron star mergers, and two neutron star-black hole collisions have been observed.